
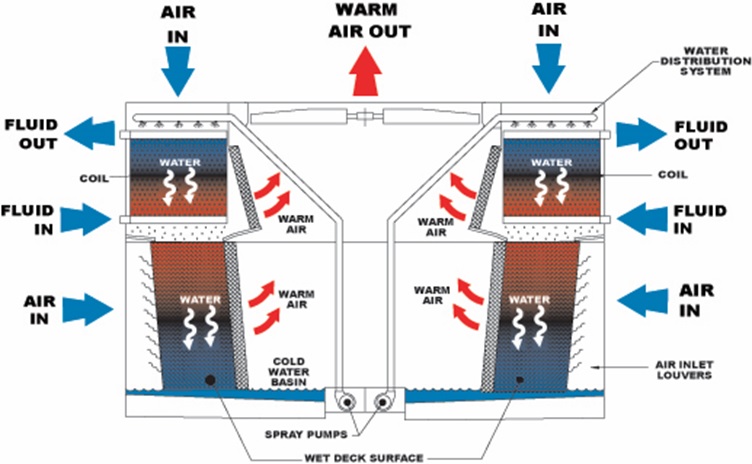
Wet surface air condensers use a tubular bundle to condense process vapors on the inside of the tubes. The exterior of the tube bundle is sprayed with water to reject heat directly to the atmosphere using latent heat transfer. Wet surface (hydrocarbon) condensers are used in a variety of industrial markets to provide lower condensing temperatures and reduce compressor horsepower by condensing the refrigerant or vapors as a direct approach to ambient wet bulb.
Applications:
- Hydrocarbon Refrigerant Condensing
- Vapor Condensing
- Ammonia Condensing
- Standard Refrigerant Condensing
Co-current flow:
Air and water flow in the same direction over the outside of the tube bundle.


Co-current flow of air and water downward over the tube bundle help to evenly distribute water over the entire tube bundle. Heat rejection is accomplished effectively and efficiently.
Combined Flow:
Combines the benefits of cooling tower and heat exchanger into one unit. Water that is sprayed over the tube bundle is further cooled using a fresh ambient air inlet. This helps to further suppress process temperatures as close to the wet bulb as possible achieving the coldest possible process outlet temperature. Additional benefits include:
- Coldest process outlet temperature
- Direct approach of the process to the ambient wet bulb
- Reduced operating horsepower
- Smaller foot print
Installed Equipment:

Please contact Engineered Thermal Solutions for more information.
